Research Topic 2
Research Topic 2 (RT2) delves into the realm of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), a collection of computer algorithms used to simulate and study how fluids like air and water move and interact with other objects or with each other. CFD is a cornerstone in modeling processes from various domains—industry, medicine, and even the environment: accurate prediction and understanding of fluid flows are essential for refining processes and elevating the efficiency of real-time simulation and Digital Twins. Yet, confronting the intricate nuances of fluid dynamics poses considerable computational challenges.
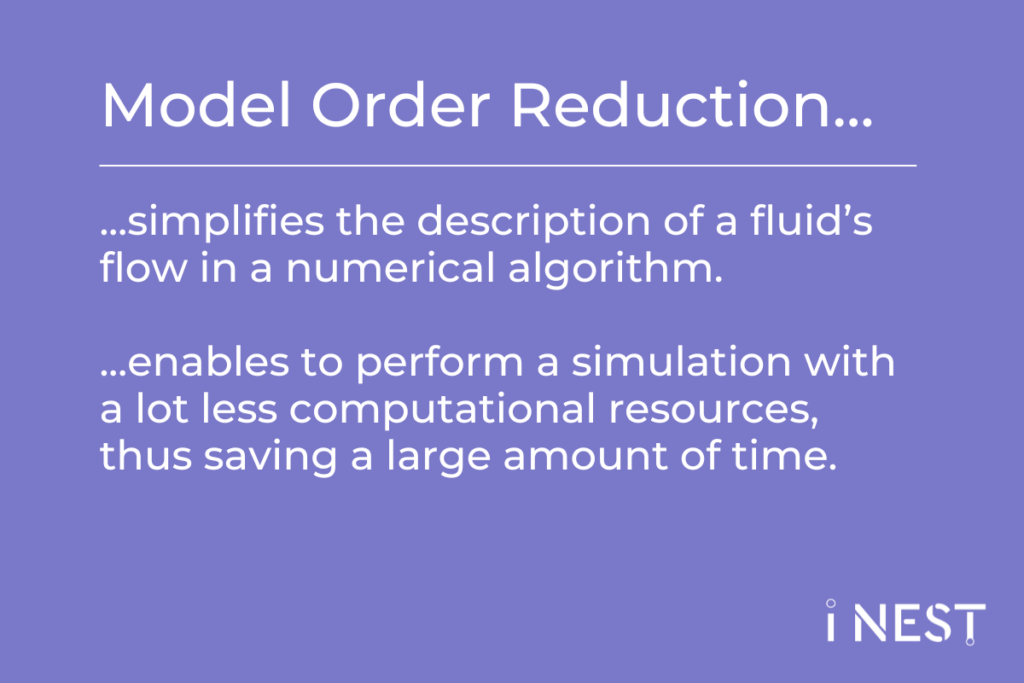
In response to these hurdles, RT2 explores the potential of Model Order Reduction (MOR) techniques. By offering a streamlined portrayal of flow behavior, MOR techniques pave the way for swift simulations and accelerated decision-making. The quest for effective representation of complex flow dynamics while achieving substantial computational savings drives RT2 to the integration of Deep Learning (DL), a collection of AI techniques that use many layers of interconnected algorithms to progressively extract more advanced features from the initial data.
Research Topic 2 is crucial for other Spoke 9 research activities: its advancements build upon foundational frameworks established by RT1 and facilitate real-time data processing that is needed for the AI-driven techniques explored in RT3. The scalable models of RT2 also ensure the seamless integration of the practical applications of DTs developed in RT4 into real-world scenarios. At the heart of RT2 lies the mission to refine DT capabilities by devising strategies that dramatically reduce computational burdens without compromising simulation accuracy.
MOR techniques: some remarkable achievements
Naval industry

- Optimization of the shape of passenger ships to reduce fuel consumption and pollution
- Optimization of ship structures for minimal material usage while maintaining stability
Environment

- Study of the impact of pollutant diffusion in the Gulf of Trieste on marine ecosystems, considering factors like sea currents and wind
Medicine

- Real-time patient-specific diagnostics for cardiovascular diseases
Other sectors

- Food waste minimization
- Appliance optimization
- Early detection of structural damages in tunnels
Participants
The participants of Research Topic 2 are the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA), the University of Padua (UniPD), and the National Institute of Oceanography and Experimental Geophysics (OGS).
The leader is Prof. Gianluigi Rozza from the International School for Advanced Studies.




